Last updated on March 23rd, 2024 at 05:14 pm
This Transistor is a popular PNP bipolar junction transistor used in low power and current, medium voltage applications. It is widely used for low-power amplification and switching.
2N3906 is complementary to the 2N3904 NPN bipolar junction transistor.

It has a current rating of 200 mA, a voltage rating of 40 V, and a power rating of 625 mW. It provides a current gain of 100 when the current of 10 mA flows through the collector. It is popular due to its high gain and low saturation voltage.
Note: The 2N3906 transistor was first manufactured by Motorola.
Table of Contents
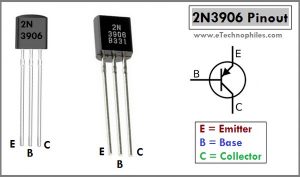
2N3906 Transistor Pinout

The pinout has three pins: emitter, base, and collector respectively from left to right(flat side with the leads pointed downward).
Specifications
| Feature | Value |
| Type | PNP |
| Package(THT) | TO-92 |
| Collector-Base Voltage | 60 V |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage: | 40 V |
| Emitter-Base Voltage: | 6 V |
| Collector Current: | 0.2 A |
| Collector Dissipation – | 0.625 W |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 100 to 300 |
| Transition Frequency | 300 MHz |
| Noise | 5 dB |
| Junction Temperature Range | –55 to +150 °C |
Equivalent
Given below is the list of popular transistors that can be used as a replacement for 2N3906
- BC557
- BC527
- BC558
- BC559
- 2N2907
- BC556
- A1015
- C945
- 2N4403
- 9014
Datasheet
This transistor is available in Through-hole and a wide variety of SMD packages(SOT23, SOT223, etc) with TO-92 being the most popular one. 2N3906 is called MMBT3906 in SOT23 or SMD package. Or in other words, MMBT3906 is the SMD version of 2N3906.
Given below is the datasheet of the 2N3906 transistor in the TO-92 package:
Electrical characteristics, current-voltage ratings, and physical dimensions are given in detail in this datasheet.
Given below is the datasheet of 2N3906 (MMBT3906) in the SOT23 package:
Where to buy?
2N3906 TO-92 Package dimensions
Below is the image of the 2N3906 TO-92 package dimensions. All the dimensions are in mm.

2N3906-based electronics projects
Low light detector using 2N3906 with LDR
This circuit detects the low light by turning ON the LED connected between the collector and the Ground. During low light in the surroundings, emitter current flows from the emitter to the collector to the Ground lighting up the LED on its way.

In the circuit diagram given above, the transistor is used as a switch to turn ON/OFF an LED(depending on the surrounding light) connected at the collector terminal. The complete circuit is powered via a 9 V supply.
A resistor of 5.6 K Ohm is connected between the load(LED) and the Ground to protect the LED from overcurrent. The required resistor value can be easily calculated using Ohm’s law.
When the light falling on the LDR is significant(low resistance), the base of the transistor is not biased. And zero -ve current flows to the base of the transistor. Due to this, the remains are in the cut-off state and the LED does not glow.
When low light falls on the LDR(high resistance), the base of the transistor is biased, and -ve current flows to the base of the transistor. Due to this biasing current, the transistor goes to the saturation state and the LED turns ON.
FAQs
What is the use of 2N3906?
This transistor is commonly used for amplification, switching, and voltage regulation in electronic circuits.
What is the maximum base current of 2N3906?
The maximum base current (IB) for this transistor is 5mA
How does a 2N3906 work?
The transistor acts like a current switch. A small base current turns on a much larger collector current, amplifying it. By controlling the base current, you can turn the transistor on (current flows) or off (blocks current). Imagine it as a tiny valve controlled by a weak signal.