Last updated on March 26th, 2024 at 12:06 pm
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor that utilizes an electrolyte to achieve a larger capacitance than other capacitor types. These are often used when high-charge storage is required in a small volume. In this article, we will discuss their classification, construction, and uses.

Table of Contents
What is an electrolyte?
An electrolyte is a liquid or gel that acts as an electrical conductor and contains a significant amount of current-carrying ions.
In electrolytes, ions can either be cations (+) or anions (-). The proton has a positive charge, whereas the electron has a negative charge. When an ion has more electrons than protons, it is referred to as an anion. Therefore anion is negative. On the other hand, a cation has a positive charge because there are fewer electrons than protons in it.
When a voltage is applied across the electrodes of the capacitor, the ions in the electrolyte flow from one electrode to the other, creating an electric current. This current creates an electrostatic field that stores energy in the form of an electrostatic charge. The amount of charge that can be stored in it is determined by the size of the electrodes and the type of electrolyte used.
Note: At temperatures of up to 85°C, medium to high voltage capacitors use ethylene glycol (EG) or boric acid as the electrolytes.
Electrolytic capacitor symbol
The symbol is shown in the figure below. One straight line and one curved line, or two parallel straight lines, are used to denote it. To indicate whether a drawn line is a positive or negative terminal, a plus or minus sign is written close to that line (anode or cathode).
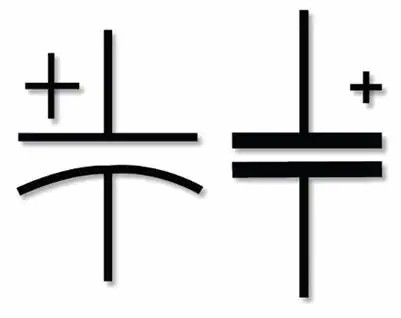
These with non-solid electrolytes have a polarity marking on the cathode (minus) side, with a shorter lead, while those with solid electrolytes have a polarity marking on the anode (plus) side, except for cylindrical led (single-ended) and SMD polymer capacitor.
Note: Applying as little as 1 to 1.5 volts in reverse polarity may damage the capacitor.
Types

These may be categorized based on the various metal types and shapes of the anode valve, the voltage level, the packaging type or electrolyte forms, the use of the capacitor, and the working environment. The list below shows all the types .
Based on anode valve metal:
- Aluminum
- Tantalum
- Niobium
Based on the shape of the anode metal:
- Foil
- Sintered
- Tantalum wire
- Aluminum sheet
Based on electrolyte form:
- Liquid
- Dry
- Solid
- Non-solid
Based on the capacitor shape package:
- Fully sealed
- Non-sealed or semi-sealed
Based on working voltage:
- Ultra-low-voltage
- Low-voltage
- Medium-voltage
- High-voltage
- Ultra-high-voltage
Based on polarity:
- Bullhorn or bolt-type
- Bipolar electrolytic
Based on working environment and usage:
- Normal temperature (-40℃~+85℃)
- High temperature (above 105℃)
- Wide temperature (-55℃~+125℃)
Other capacitors:
- DC
- High-ripple
- AC (such as single-phase motor start)
- High-voltage energy storage
- Low-frequency power amplifier
- Camera flash
- Laser energy
- Electromagnetic ejection
- Electromagnetic railgun
How is an electrolytic capacitor constructed?
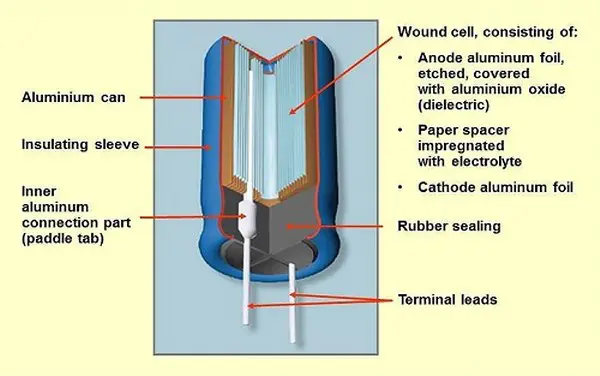
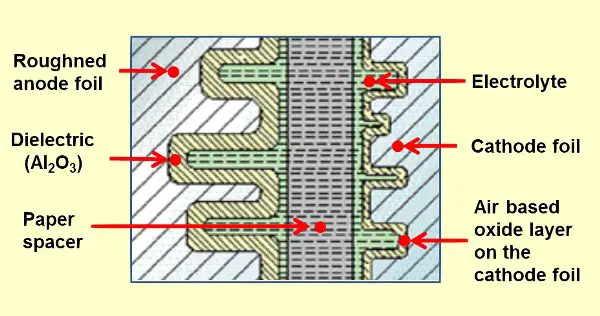
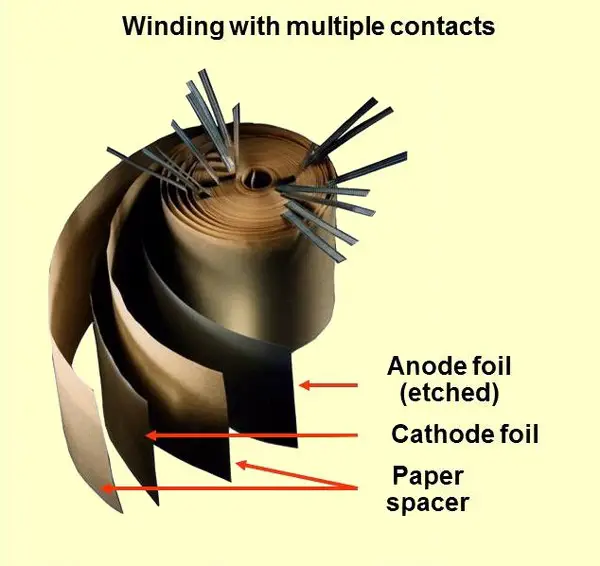
These consist of a cathode, anode, dielectric layer, and an electrolyte. The anode is made of metal. Common metals used for the anode are Aluminium, tantalum, and niobium. The dielectric material is produced from the anode metal itself through the process of anodization.
So formed dielectrics are aluminum oxides, tantalum pentoxide, and niobium pentoxide respectively. The electrolyte of the capacitor can be solid, liquid or gel. This electrolyte covers the oxide layer and acts as the cathode.
Due to this enlarged anode surface and very thin dielectric oxide layer, electrolytic capacitors can have a high capacitance voltage per unit volume. Hence they can have a high capacitance value.
The capacitance of electrolytic capacitors ranges from 1µF to 47000µF.
Advantages
- They are used to achieve a high capacitance value for a given volume.
- It is mostly suitable for low-frequency applications.
- Tantalum-type electrolytic capacitors have higher stability.
- Electrolytic capacitors possess a very wide tolerance.
- They are relatively cheaper when compared to other types of capacitors with similar capacitance values.
- It helps in quick charging and discharging.
- Minimal maintenance is required for proper functioning.
- Electrolytic capacitors have self-healing capability.
Self-healing is the ability of a capacitor to recover itself when subjected to some problems during normal operation
Disadvantages
- They have high leakage current and wide tolerance which limits their range of applications.
- It must be ensured that these capacitors are connected with proper polarity or else they will explode.
- Reverse voltage damages it.
- The performance may easily be affected due to temperature changes.
- It has a limited lifespan.
- They are not suitable for AC applications.
- They are not capable of withstanding overvoltages.
Applications
They are used in areas where tight tolerances and AC polarization are not required but large capacitance values are required. They are mainly used for:
- Preventing voltage fluctuations in different filtering devices.
- Used as an input-output smoothing filter.
- Used for filtering noise or decoupling in power supplies.
- Helps in controlling the coupling of signals between amplifier stages.
- Storing energy in low-power applications or in flashlamps.
- To provide time delays between two functions in a circuit.
- Used as filters in audio amplification circuits to reduce hum.
FAQs
What is the principle of an electrolytic capacitor?
An electrolytic capacitor works like a regular one, storing electrical energy by separating charges in an electric field.
Are electrolytic capacitors AC or DC?
Electrolytic capacitors are specifically for DC (Direct Current) applications.
