Last updated on April 5th, 2024 at 04:55 pm
Both lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries. As per the timeline, lithium ion battery is the successor of lead-acid battery. So it is obvious that lithium-ion batteries are designed to tackle the limitations of lead-acid batteries.
Although lithium-ion batteries have replaced lead-acid batteries in some applications, both these types are being actively used today. Let us make a comparative study based on their characteristics.
Table of Contents
Lithium-ion vs Lead acid battery- Which one is better?
Lithium-ion batteries are far better than lead-acids in terms of weight, size, efficiency, and applications.

Lead-acid batteries are bulkier when compared with lithium-ion batteries. Hence they are restricted to only heavy applications due to their weight such as automobiles, inverters, etc.
The major advantage of lithium-ion batteries is that they are available in numerous sizes and capacities. So they are used in a variety of applications such as mobile phones, laptops, electric vehicles, solar power, etc.

Lithium-ion batteries also have a longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries. Thus, when considering all the factors, lithium-ion batteries are better than lead-acid batteries.
However, lead-acid batteries still have their own advantages. They are less expensive than lithium-ion batteries and can be used for high-current applications. Now let’s look at the differences between them in detail.
Battery chemistry and working
Since both are constructed with different chemical compositions, they also vary in their internal working and chemical reactions happening inside. As they are secondary batteries, the chemical reactions happening in both are reversible. This makes it possible to recharge them.
Battery composition
Both anode and cathode of lead acid battery are lead compounds and sulfuric acid is used as an electrolyte. Whereas in the lithium-ion battery, the anode and cathode are lithium compounds and an organic compound with lithium-ion is used as an electrolyte.
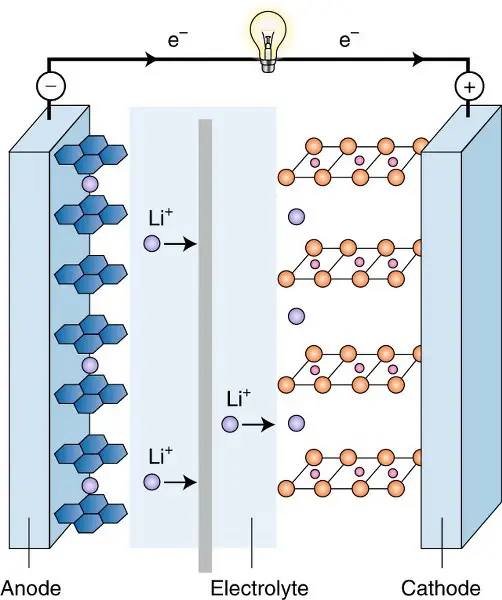
Battery structure
The lead acid battery comes in the regular battery structure where the electrodes are dipped in the electrolyte. But the lithium-ion battery has a slightly different arrangement. The battery is made of two half-cells and both are filled with electrolytes. They have a separator in between. One-half cell is the anode and the other is the cathode.
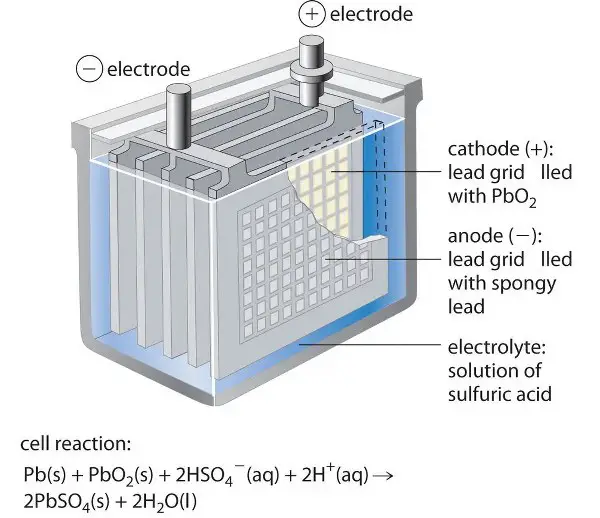
How do discharging and charging processes differ?
During the discharge in lead acid batteries, the lead sulfate is formed by the reaction of lead and sulfuric acid. This releases free electrons which flow through the circuit. In the case of lithium-ion batteries, lithium-ion and free electrons are released from the electrolyte, in which both move from the anode chamber to the cathode chamber.
The lithium ions can surpass the separator but the electrons move through the circuit, resulting in an electric current. The exact reverse of these reactions happens in both the batteries while they are connected to the charging circuit. The compounds get back to their initial form.
Note: Complete discharge is not appreciated in both the batteries since it causes wear out of the electrodes and reduces battery capacity.
Battery capacity: Lithium-ion vs Lead acid
Capacity is one of the essential features of any battery. There are several definitions for capacity. Battery capacity can be defined as the total amount of electricity generated by the battery due to chemical reactions. It is measured in Ampere-hours (Amp-hr).
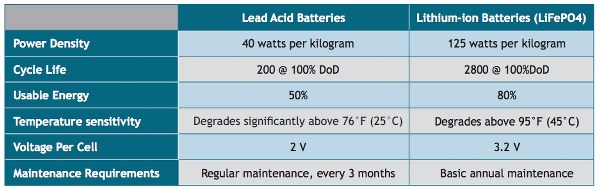
**Image courtesy: Data Center Frontier
Capacity is one of the important difference between Lead-acid and Lithium-ion battery.
Lithium has 29 times more ions per kg compared to that of Lead. For example, when two lithium-ion batteries are required to power a 5.13 kW system, the same job is achieved by 8 lead acid batteries.
Hence lithium-ion batteries can store much more energy compared to lead acid batteries. Thus the former has a very high capacity per unit volume compared to the latter.
Which has a higher energy density?
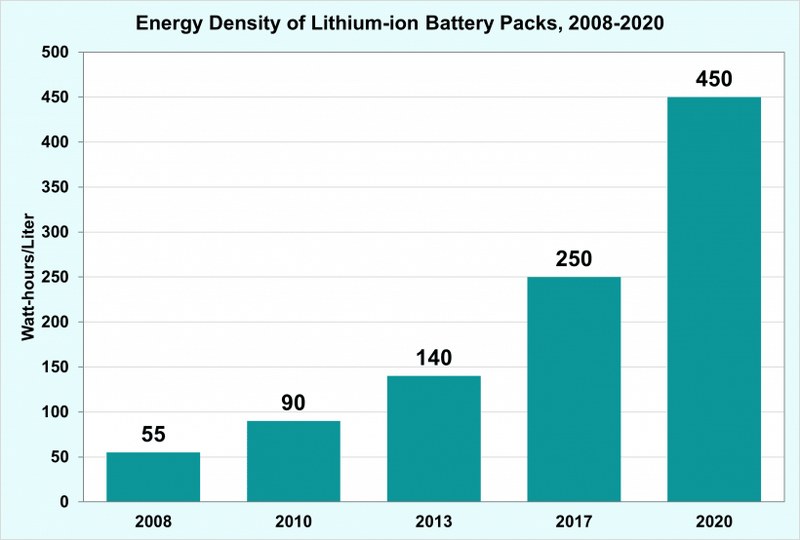
Energy density denotes the amount of energy delivered by the battery relative to its weight. It is measured in watt hours per kilogram (Wh/kg) or watt-hours per liter (Wh/l). This is another favorable feature of lithium-ion batteries when compared to lead-acid batteries.
The energy density of lithium-ion batteries falls under the range 125-600+ Wh/L whereas, for lead acid batteries, it is 50-90 Wh/L.
This drastic variation is due to the fact that lead acid batteries are much heavier than lithium-ion batteries, which in turn results in less energy density. Lead acid batteries also need more space to fit in. Thus lithium-ion batteries offer more storage capacity in less space when compared to lead acid batteries.
Durability
The durability of secondary batteries is usually indicated in terms of the number of charge-discharge cycles. When the battery is charged completely and used up to its permitted discharge level, it is known as one cycle. Durability is another major difference between Lead acid and lithium ion battery.
Lithium-ion batteries admit 10,000 charge cycles and a life of 10 years when they are discharged up to 70% of their initial capacity. This is very high compared to that of lead acid batteries since they only offer 350 cycles and a life of 1 year when discharged up to 70%.
Charge-discharge speed
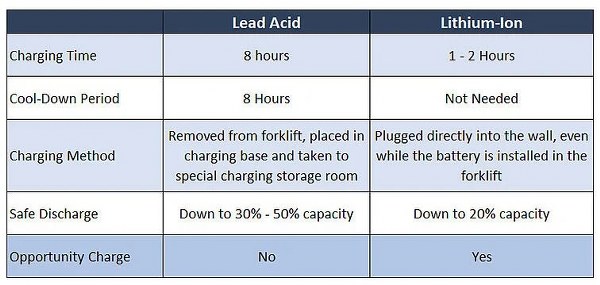
The time required for a battery to get fully charged and how quickly they drain out are other two important concerns. A battery with quick charging but longer discharging time is highly preferred in the market.
**Image courtesy: FluxPower
Lead acid batteries require a long charging time ranging from 6 to 15 hours, while lithium-ion batteries take 1 to 2 hours to charge up to 80%. This range may slightly vary depending on the power output. Both make a quick discharge and are capable to provide large currents if required.
Which is safer?
Both batteries are generally considered safe if used under the recommended conditions. Overcharging is considered the most restricted practice in the case of batteries. This increases the chance of thermal runaway which is the major cause of caution while handling them.
Thermal Runaway: Battery overcharging increases temperature. This leads to a rapid release of energy that further increases temperature and can even lead to an explosion.
This property is applicable to both battery types. However, since lithium-ion batteries are far denser than lead-acid batteries, their degree of damage is the highest. It may even lead to violent explosions.
The thermal runaway may also result in short circuits that cause damage to all the connected devices.
This issue is a serious concern for these batteries. Hence an intelligent battery management system is mounted to them, especially for lithium-ion batteries. This system monitors the voltage, current, and temperature and stops the charging process in case of any severe variations.
Which battery type can be safely disposed of?
The safe disposal of lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries is a serious concern since both batteries contain hazardous and toxic compounds. Improper disposal results in severe pollution.
The best-suggested option for batteries is their recycling and reuse. It is also helpful in replacing the resources as the demand for these batteries rises. Heavy demand is resulting in depletion of resources.

Lead acid batteries take the highest position in reusability since 90% of the battery material can be recycled. The recycling infrastructure of these batteries are well established and actively functional. Most of the recycled versions are used in automobiles.
Compared to these, the recycling and reuse of lithium-ion batteries is not popular. But since lithium is a highly poisonous and volatile material, the disposal of batteries is very risky and performed with extra care using different methods.
Thus recycling and reuse are the most recommended action over disposal. The recycling methods of lithium-ion batteries exist but the more efficient methods are under research. (Read more)
Price comparison
Lead acid batteries are currently the most cost-effective rechargeable batteries on the market. The large current requirement can be met at a low cost with these batteries. But in the case of the cost relative to power and efficiency, lithium-ion batteries become the better choice.
The Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS) is a parameter used for the comparison of the cost of different battery technologies. It is expressed in USD/kWh. It considers all the expenses related to energy storage over the lifespan of a battery.
If the cost is directly considered, lithium-ion batteries cost more than double the cost of lead-acid batteries for similar performance. For example, when lead acid batteries were available for $50, lithium-ion batteries were priced at nearly $150. But gradually, the cost of lithium-ion batteries is falling down every year.
When considered in terms of LCOS, lithium-ion batteries lowest values compared to lead acid batteries. This is due to the heavy energy storage capacity and lifespan of lithium-ion batteries.
Weight difference
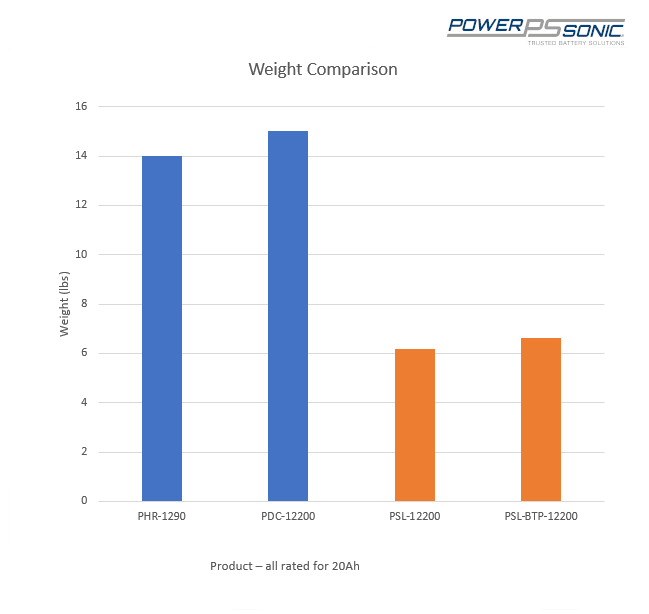
The concern of battery weight is highly relevant in some specific applications. The major drawback of lead acid batteries is their weight. It is bulky and requires more space whereas lithium-ion batteries are available in coin size also.
**Image courtesy: PowerSonic
The lithium-ion batteries are about 10 times lighter compared to their lead-acid counterparts. This advantage of lithium-ion batteries is the major reason for their utilization in EV sector. The EV’s were powered by lead-acid batteries in the initial period. Now they are almost completely replaced with lithium ions.
Applications
The choice among batteries is made according to their various features. But when we compare the applications of lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries, the usage of lead-acid batteries is restricted only to heavy applications since they are bulky. It also requires more space to accommodate.

- Lead-acid batteries are used as ignition power sources in automobiles, power storage such as UPS systems, marine applications, etc.
- Although these batteries are bulky, they are well-suited for high current-drain applications like large and grid-scale power systems, emergency supply on ships, etc.
**Image courtesy: ResarchGate
- Lithium-ion batteries on the other hand are available in numerous sizes and capacities. So they are utilized in a variety of applications. The major application of these are in mobile phones and laptops.
- Currently, the most popular application is to run electric vehicles and batteries in solar power. They are now being utilized in almost all portable applications.
FAQs
What is the average lifespan of a lithium-ion battery?
On average, lithium-ion batteries typically last between 2 to 3 years or 300 to 500 charge cycles before experiencing notable degradation in performance.
How long does a lead-acid battery last?
Lead-acid batteries can last anywhere from 3 to 5 years under normal operating conditions. However, with proper care and maintenance, such as regular charging, avoiding deep discharges, and ensuring proper ventilation, they can potentially last longer.
