Last updated on March 23rd, 2024 at 12:18 pm
OBD2 is a second-generation onboard diagnostic system installed in cars that collects data from various parts of the car. It is the vehicle’s automotive term that monitors RPM, emissions, mileage, horsepower, speed, and other parameters of your car.
The Check Engine light in your car, connected to this OBD2 system, illuminates when it detects a problem. A technician then checks the error report, by connecting an OBD scanner to the OBD2 port in your car. This data helps the technician in determining the overall health of the engine, battery, etc.
The word OBD2 originates from the term OBD.
Here are 10 facts you should know about OBD2 starting with the definition and working of OBD
Table of Contents
What is OBD and how does it work?
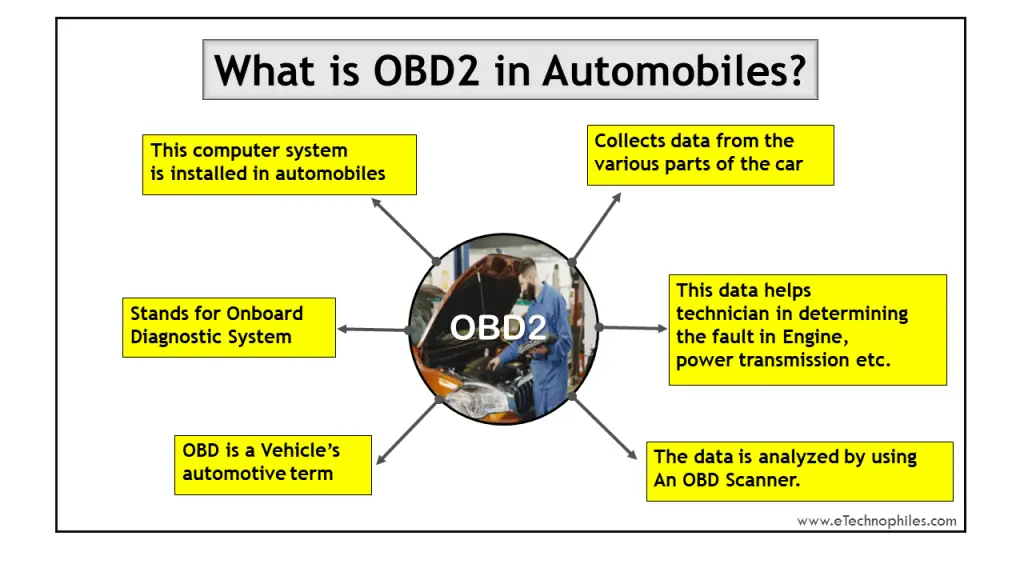
OBD stands for onboard diagnosis which is nothing but a computer system installed in cars. This OBD system provides an error report to the owner of the vehicle or a technician with the help of data & the info obtained from vehicle sub-systems.
OBD is self-diagnostic and reports its capability in the vehicle’s power transmission, engine & other subsystems. In other words, it is the process of scanning a vehicle with an onboard diagnostic system.
The sensors inside the vehicle give information to the embedded system & the computer which is used in optimizing car systems or show a warning to the owner/technician about the fault which can be used in diagnosing the problem.
Nowadays, the OBD system provides real-time data with the help of a standardized digital communications port with diagnostic trouble codes, or DTCs, which allows for identifying the issue and rectifying malfunctions in the vehicle promptly.
How many versions of OBD are there?
As of now, there are only two versions of OBD: OBD1 and OBD2. OBD1 is the first version that was introduced in 1991 for commercial cars. Whereas OBD2 is the latest generation diagnosis system that is more advanced, efficient & successful as compared to its predecessor.
OBD1 does not support all former models, however, it only supports cars manufactured before 1996.
From 1st January 1996 onwards, OBD2 was made compulsory for commercial use.

Is OBD1 better than OBD2?
No, OBD2 is better than OBD1 because it gathers data from more parts of the vehicle, has a higher processing power than OBD1, and is globally accepted. OBD1 only collects the critical data from the engine, whereas OBD2 collects the data from the engine, power transmission, battery, and other parts of the vehicle.
OBD1 was not successful because obtaining information from specific diagnostic parameters was not standardized back then. This led to irregular testing of vehicles.
For example, an OBD1 scanner that works for Toyota wouldn’t work for Ford.
OBD2 is an improvement over OBD-I in terms of both standardization & efficiency.
In an OBD2 system, the scan tool gets power from the vehicle battery through a pin in the connector. Thus the requirement of connecting a scan tool to a power source gets eliminated.
Although, the scan tool can be connected to an auxiliary power source if a vehicle faces a loss of electrical power due to some breakdown.
For standardization in the OBD2 system, different vehicle manufacturers have already made the DLC (Diagnostic Link Connector), the only main component through which all emission-related codes & programmable data are transmitted & the issues are diagnosed simultaneously.
OBD1 VS OBD2: key differences
Based on parameters, the differences between OBD1 and OBD2 are explained below.
| Parameters | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Type of car | Suitable for 80’s car model as well as for the cars that were introduced before 1995 | Supports those cars which were introduced in or after 1996 |
| Installation method | It connects to the console | Wireless (via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth) |
| Accuracy | Low | Higher |
| Technology | Not sufficiently advanced | Highly advanced technology |
| Functions | It checks only sensors and actuators maintained in the vehicle. | Along with OBD1 functions, it can check performance level, shows a graphical representation of data, smog tests, battery usage, etc. |
| Standardization | Poor, a single OBD1 unit can support different only one manufacturer. | Excellent, a single OBD2 unit is suitable for different manufacturers. |
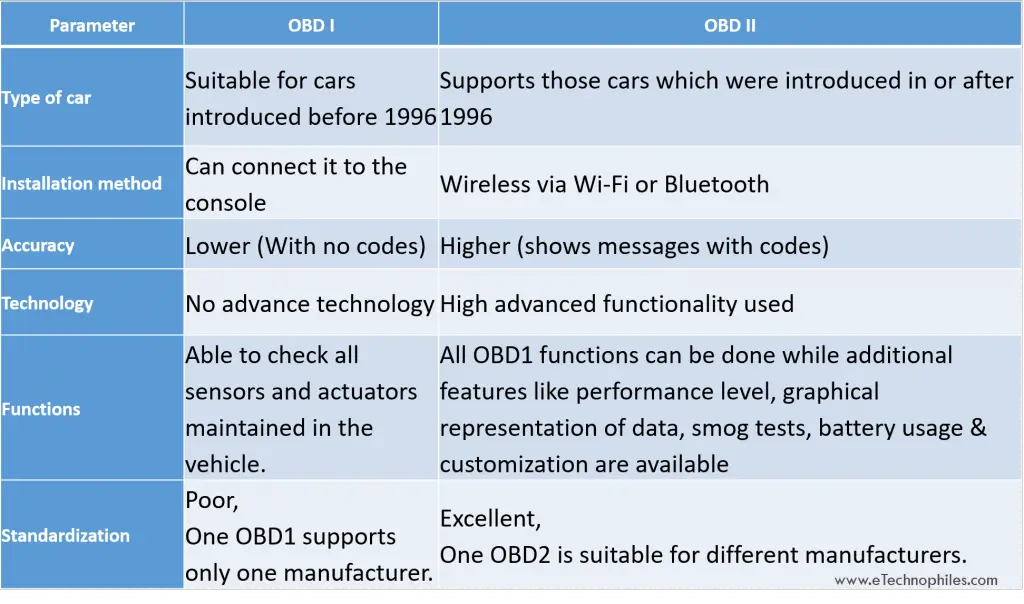
From the above table, we get an idea of the difference between the two OBDs. Now let’s move further and look at OBD2 in detail.
What is an OBD2 port in cars?
To collect data from the OBD 2 system, it is essential to connect an OBD 2 scanner to it. That’s why there is a 16-pin OBD 2 port inside the vehicle, usually placed under the driver’s side dashboard. And to connect an OBD scanner to this port we need an OBD connector.
Are there any types of OBD2 connectors?
Yes, there are two connectors available for OBD2: OBD-IIA and OBD-IIB. The former connector is used for small cars, while the latter is used in medium and heavy-duty vehicles.
What is an OBD scanner?

An OBD scanner or scan tool is a device for vehicle diagnosis. Using it, error memory and data can be read from the vehicle systems. There are certain standardized codes(DTC) for the errors generated by the OBD system or computer. An OBD scanner can decode these codes to detect any particular error.
These codes are called Diagnostic Trouble Codes or DTCs.
OBD 2 scanner creates a connection between diagnostic software or a mobile app and a car. Through this, all the car’s data like engine fault reports are accessed from the scanner. And in some cases, a car’s control can be achieved through coding.
OBD scanners are the most convenient device & some of their advantages are:
- Small & compact size (unlike heavy OBD cables or handheld scanners)
- User friendly
- No additional requirement of diagnostic equipment (like cables, computer software, etc.)
- Multifunctional.
What are DTC codes?
We use DTCs or Diagnostic Trouble Codes to determine the problem in the Vehicle’s subsystems. These DTCs are read by the OBD scanner which then decodes them to reveal the problem.
For example, an electronic control module uses an oxygen sensor to monitor exhaust gas for being rich or lean.
If the computer feels like the sensor conditions are not optimum, and there is a risk of malfunction, it sets a DTC for this error and turns ON the check engine light.
There is a complete list of DTCs for OBD2.
What are the components of OBD system?
OBD system consists of a central unit, indicators, sensors, and a connection point. Let’s see the function of each component in the OBD system.
- ECU: It stands for Electronic Control Unit. It collects input from various sensors present in every part of the vehicle.
- Sensors: The interconnected sensors in the vehicle send codes to the ECU if it detects any error.
- DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code. DTC consists of various numbers & letters which give a brief about the problem.
- MILs: Malfunction Indicator Lights. These are the indicator lights that give an early alert for any faults in the vehicle.
- DLC: Diagnostic Link Connector, generally found beneath the car’s dashboard on the driver’s side.
How to find the OBD2 port in your car?
An OBD port or diagnostic port location varies from manufacturer to manufacturer. Generally, it is found on the driver’s side, under the dashboard. In some vehicles, it is present near the center console section of the vehicle.

In old models, this port is present near the handbrake or in the trunk.
After finding this port, we can easily plug the scanner into it. This way, we can establish a connection between the vehicle and the diagnostic device.
FAQs
Are OBD2 scanners safe?
OBD2 scanners are generally safe tools designed to access diagnostic information from a vehicle’s computer system. When used correctly and with caution, they pose minimal safety risks.
Can I use OBD2 while car is running?
Yes, you can use an OBD2 scanner while the car is running. It’s often recommended to do so, as it allows the scanner to access real-time data from the vehicle’s computer system,
Does OBD drain battery?
OBD2 scanners draw a small amount of power from the vehicle’s battery but generally do not significantly drain it, especially during short diagnostic sessions.

