Last updated on March 26th, 2024 at 04:51 pm
A diode is a device that allows the flow of current in one direction only. They are of many types, but the most popular one is a Rectifier diode. In this article, we will discuss what it is, where it is used, and some of its popular types.
Table of Contents
What is a rectifier diode?

It is a general-purpose P-N junction diode that is used to eliminate the negative half cycle of the input AC supply. To put it simply, a diode that can be used in a rectifier circuit is called a Rectifier diode, hence the name.
Now every diode type can be used to rectify the input voltage since they all block the current flow in the opposite direction (fundamental behavior). However, certain parameters or specs make them suitable for rectification purposes. For example, a rectifier diode has a high reverse voltage and low leakage current ratings.
So it is manufactured in such a way that it can be used in rectifier applications, AC to DC supply for example.
Diodes like Schottky and Zener diodes can also be used as rectifiers but they have low voltage and power ratings and high leakage current, etc. Plus they have their applications. So why use them when we already have a diode for this specific purpose, i.e., the rectifier one?
Symbol
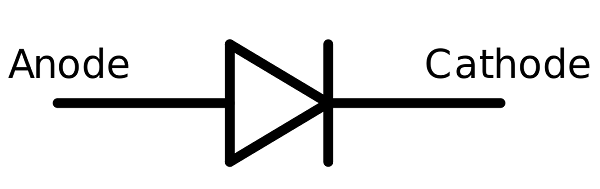
Since it is a PN junction diode, its symbol is a triangle pointing to a straight line. The triangle shows the direction in which the diode allows the current flow i.e. towards the straight line. The base of the triangle is the Anode or positive terminal and the line is the Cathode or negative terminal.
Where are rectifier diodes used?
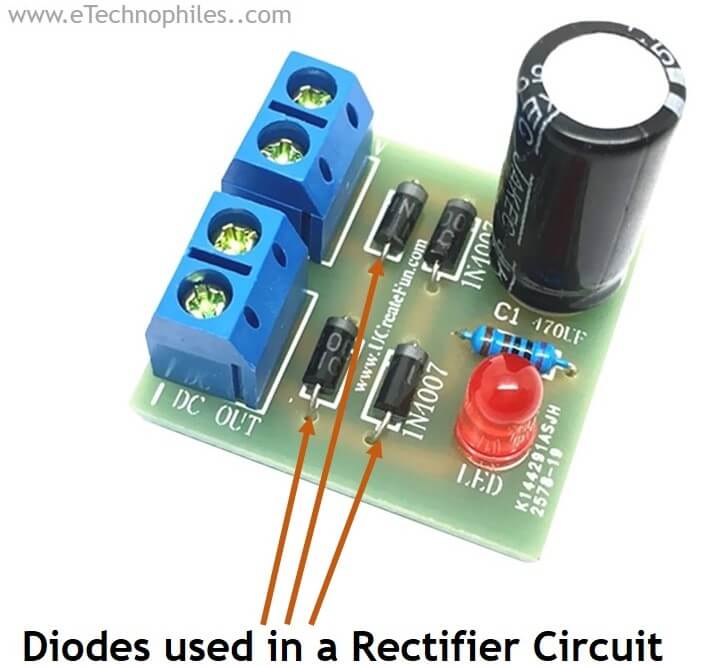
These are used in a variety of applications, including power supplies, adapters, battery chargers, voltage doublers, and signal rectification. They are also commonly used in automotive electronics, as they can withstand high temperatures and vibrations.
They can be used in both AC and DC circuits, making them versatile components for a wide range of electronic devices.
Their main purpose or application is in rectifier circuits due to ratings and characteristics.
Ratings
Forward voltage drop: The typical forward voltage drop is 0.6 V to 0.8 V.
Peak repetitive reverse voltage: The maximum reverse voltage that can be applied to it can go up to several kilovolts. For example, VRRM for 1N4007 is 1000 V.
Operating Temperature: These are made to withstand extreme temperatures. For example, Tj for 1N4007 is -65 to 125 °C.
Power ratings: Their power handling capability depends on the forward voltage drop and current rating i.e. P = V x I. For rectifier diodes, it can go up to several watts.
Some popular rectifier diodes
The most common type of rectifier diode is the 1N400x series. These are available in a range of voltage ratings, from 50 volts to 1,000 volts. They are also widely used in power supplies, as they have a low forward voltage drop and can handle large currents.
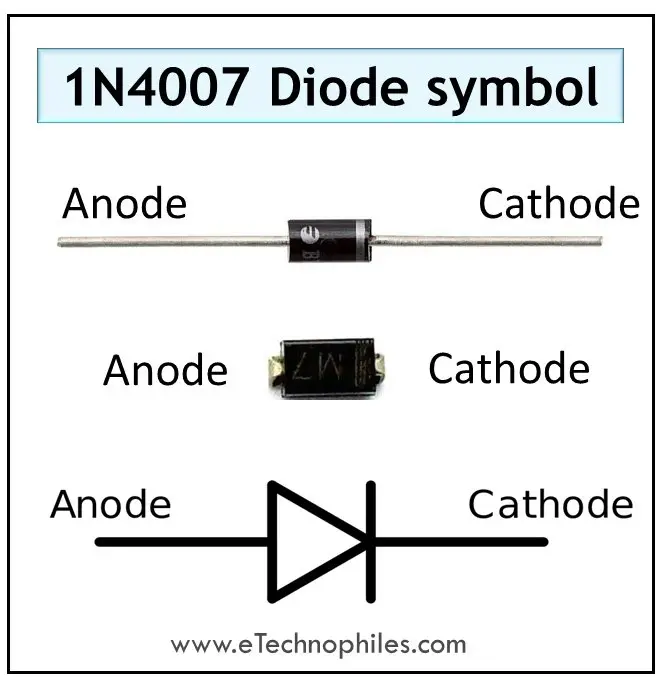
The other popular rectifier diode is the 1N54xx series. These have a higher average forward current and low leakage current.
| Diode name | Peak reverse voltage | Max. forward current | Max reverse current | Peak surge current | Max voltage drop |
| 1N4001 | 50 | 1 A | 0.03 mA | 30 A | 1.1 |
| 1N4002 | 100 | 1 A | 0.03 mA | 30 A | 1.1 |
| 1N4003 | 200 | 1 A | 0.03 mA | 30 A | 1.1 |
| 1N4004 | 400 | 1 A | 0.03 mA | 30 A | 1.1 |
| 1N4007 | 1000 | 1 A | 0.03 mA | 30 A | 1.1 |
| 1N5402 | 200 | 3 A | 500 µ A | 200 A | 1.2 |
| 1N5406 | 600 | 3 A | 500 µ A | 200 A | 1.2 |
| 1N5408 | 1000 | 3 A | 500 µ A | 200 A | 1.2 |
As discussed above, they are mainly used for rectification purposes. Generally, there are two types of rectifier circuits: Half-wave rectifier and Full-wave rectifier circuits. We have discussed various rectifier circuits and their working in this article.
FAQs
What is the difference between a diode and a rectifier?
A diode permits current in one direction, blocking it in reverse, useful in voltage regulation, rectification, and circuit protection. A rectifier, made of diodes, converts AC to DC by directing current flow during positive and negative half-cycles, crucial for power supplies, chargers, and welding equipment.
Is a rectifier AC or DC?
A rectifier itself is neither AC nor DC. It’s a device, specifically an AC-to-DC converter.
List three applications of rectifiers.
The three applications are:
Battery Charging: Rectifiers charge batteries by converting AC to DC.
Modulation/Demodulation & Voltage Multipliers: it is used for signal processing and voltage boosting applications.
Welding: Rectifiers provide stable DC for welding.