Last updated on December 16th, 2023 at 01:36 pm
Transistors are used in almost every electronic device today. That’s why it is called “a revolutionary electronic component of this century”.Today we are going to build an awesome Transistor Project a Rain Sensor Alarm using two transistors and a Buzzer.
A rain sensor alarm senses and gives a signal to the buzzer when water droplets from rainfall on its surface. Thus as soon as it comes in contact with water, the buzzer starts beeping.
We are going to build this rain sensor using transistors due to their high current gain capacity. This Rain sensor can sense even a small tiny drop of water. We will use two transistors to achieve this, connected as a Darlington pair. A highly sensitive Transistor-based sensor is obtained due to this Darlington pair combination.
Components required for rain sensor alarm
- BC547 transistor x 2
- Piezoelectric Buzzer
- 9v Battery
- 1k ohm resistor
- 1 uf capacitor
- 9v Battery Connector
- Metal Screw x 2
- Plastic sheet
- Connecting Wires
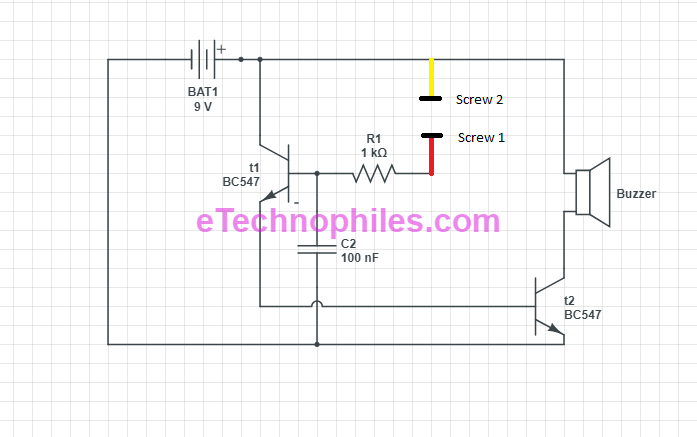
Circuit diagram
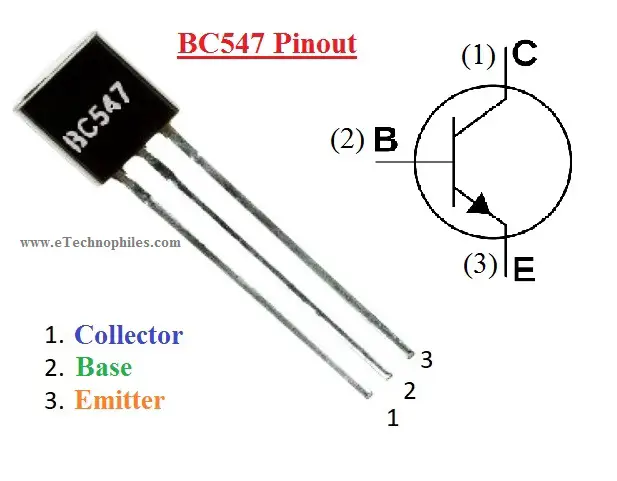
Terminals of Transistor BC547
Working of rain sensor alarm circuit
CASE 1:
- When rain falls on the plastic sheet, the circuit which was open before now becomes closed. This is due to the formation of a conduction path between the two screws caused by water. As soon as this happens:
- Current starts flowing at the base of transistor 1 which causes it to turn on.
- Now since transistor 1 is on, it acts as a close switch between collector and emitter. And current starts flowing through the collector and then the emitter of transistor 1 to the base of transistor 2.
- This flow of current to the base of transistor 2 turns it on.
- Now since transistor 2 is also on, it acts as a close switch between its collector and emitter terminal. And current starts flowing through the Battery to the Buzzer and then from Collector terminal to emitter terminal to Ground finally. Since current flows through the Piezoelectric Buzzer, it produces sound thus indicating the presence of water droplets or rain.
CASE 2:
- In the absence of rain or water droplets on the plastic sheet, the circuit remains open between the resistor and the positive terminal of the battery. This is due to the absence of a conduction path between the two screws. As soon as this happens:
- No Current flows to the base of transistor 1 and it remains off.
- Now since transistor 1 is off, it acts as an open switch between the collector and emitter. And current does not flow through the collector and then emitter of transistor 1 to the base of transistor 2.
- As no current flows to the base of transistor 2, it remains off.
- Now since transistor 2 is also off, it acts as an open switch between its collector and emitter terminal. And no current flows from the Battery to the Buzzer. Since current does not flow through the Piezoelectric Buzzer, it produces no sound thus indicating the absence of water droplets or rain.