Last updated on March 23rd, 2024 at 06:00 pm
HC-SR04 is a simple ultrasonic sensor that can measure distances up to 400 cm. The sensor has 4 onboard pins that connect to a microcontroller like Arduino.
It operates by emitting ultrasonic waves from its transmitter and measuring the time it takes for the waves to travel to an object and back to the sensor after being reflected. The transmitter transmits the sound waves whereas the receiver receives these transmitted sound waves reflected from the object in front.

It can be used with Arduino for projects like distance measurement. HC-SR04 working principle is similar to SONAR or Sound Navigation and Ranging. SONAR is used by ships to navigate the objects undersea.
Table of Contents
Before jumping into the HC-SR04 sensor working section, let’s look at its pinout.
HC-SR04 Pinout
HC-SR04 has 4 pins. Starting from left: VCC, TRIGGER, ECHO, and GND
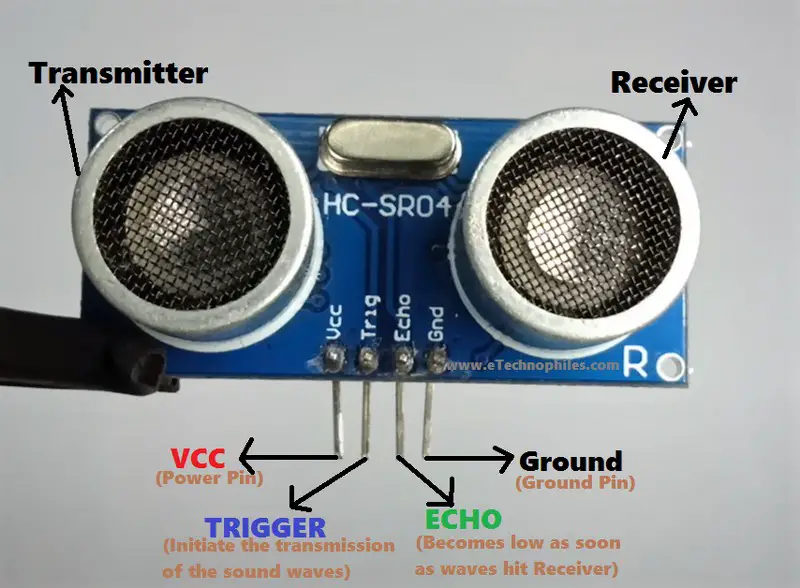

| Pin name | Function |
|---|---|
| VCC | Powers the Ultrasonic sensor. |
| TRIGGER | This pin initiates the transmission of the sound waves. |
| ECHO | Becomes low as soon as the transmitted sound waves hit the Receiver. |
| GROUND | Goes to the circuit’s ground. |
Read Also: Beginners Guide to IR Sensors
Now let’s see how the HC-SR04 distance Sensor works and measures the distance of an object.
How does HC-SR04 work?

Step 1: As soon as the Trigger pin is set to High(programmed), sound waves are transmitted from the transmitter.
Note A: At the same time, the Echo pin automatically becomes high(gives 5 V as output). Let’s say the time at this instance is t1.
Note B: The speed of the sound wave is 343 m/s
Step 2: These sound wave travels through the air and gets reflected back by the object in front of it. As soon as the waves reach the receiver, the Echo pin becomes low. Let’s call the time at this instance t2.
Step 3: Now in order to find out the distance traveled by the waves, first we have to measure the total time for which the echo pin was high(Arduino does this for us).
In other words, the echo was high for exactly the same time it took the waves to get back to the receiver.
i.e, t2 – t1 = time for which the Echo pin remains high
OR
Ttotal = t2 – t1 (total time taken by the sound waves to get back to the sensor after reflecting back from the object)
Step 4: By the distance-time-speed formula, we can calculate the total distance traveled by the wave(speed is constant).
Speed = Distance / Time OR Distance = Speed X Time
So simply multiply the total calculated time by the speed of sound. This gives us the total distance traveled by the sound waves.
Dtotal = (T2 – T1) X Speed of sound
Step 5: This(total distance) is actually a two-way distance. But we want to measure the one-way distance. And since the total distance is actually double the one-way distance, we divide it by two to get the one-way distance from the sensor to the object.
Done-way = Dtotal / 2
Of course, this calculation is done by the Arduino itself. We did this manually to show you how the distance is calculated.
Let’s understand this once again by an example.
Let’s suppose there is an object in front of the sensor at a distance of 10 cm. Sound waves are transmitted, hit the object, and then get back to the receiver.


The total time between these two events is calculated using the echo pin as mentioned earlier. Now using this formula oneway distance is calculated: Distance = Time * Speed of Sound/2
How to use HC-SR04 with Arduino?
To make the distance measurement project using an HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, I am using Arduino UNO here. You can use any other Arduino board.
First, connect the sensor with Arduino as shown below.
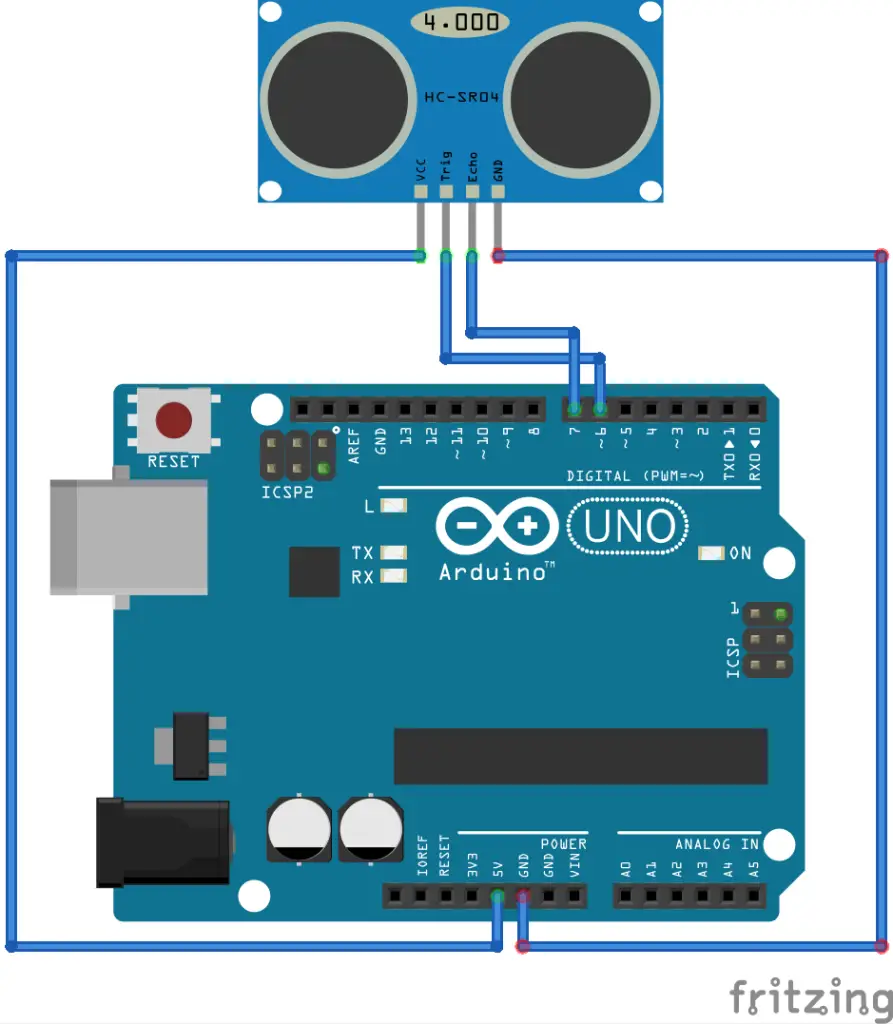
Connect the VCC and GND pins of the sensor to the 5 v and GND pins of Arduino respectively.
Connect the trigger and echo pin to digital pin 6 and echo to digital pin 7.
Program
Upload the program given below to your Arduino board.
const int trig = 6;
const int echo = 7;
long totaltime;
int distance;
void setup() {
pinMode(trig, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echo, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(trig, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trig, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trig, LOW);
totaltime = pulseIn(echo, HIGH);
distance= totaltime*0.034/2;
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.println(distance);
}Code Explanation
The code for measuring distance using an ultrasonic sensor is very simple. First, the trigger pin is set high for 10 microseconds. Then time for which the echo pin remains high is calculated using the pulse-in function. Finally, distance in centimeters is calculated using this formula:
distance= totaltime*0.034/2;
Now upload the code to Arduino and then open the serial monitor. Here you can see the calculated distance of the object from the surface of the ultrasonic sensor. Let’s move the object and see how accurate is the measurement.

