Last updated on March 21st, 2024 at 03:44 pm
NEMA 17 stepper motor is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation down into equal steps. It is suitable for applications where precise movement is required. In this article, we will discuss the NEMA-17 stepper motor, its applications, and the pinout of the motor. We will also discuss some of its technical specifications in detail.
What is NEMA?
NEMA stands for “National Electrical Manufacturers Association”. It’s an organization that sets standards for companies, manufacturing electrical products and/or equipment in various sectors.
This standardization eliminates some common misunderstandings between users and electrical product manufacturers and improves the state of electrical manufacturing.
Table of Contents
NEMA 17 stepper motor
NEMA 17 is a hybrid stepper motor that rotates with a step angle of 1.8 degrees. Thus to complete one revolution, the shaft takes 200 steps. The term hybrid signifies that it is a combination of a permanent magnet and variable reluctance stepper motor.
With dimensions, of 1.7 x 1.7 inches (42 x 42 mm), NEMA 17 steppers are engineered to provide more torque than smaller variants like NEMA 14 stepper motor.
Like every other motor, the NEMA 17 stepper motor consists of a stator and rotor. The rotor of the NEMA 17 motor is a permanent magnet with 50 teeth on its circumference. The stator is simply an electromagnet with 48 teeth.
These are arranged into four group pairs, where each group can be controlled by DC excitation. So, when we excite the stator coil pairs using a microcontroller, the rotor rotates with a smooth step angle.
Specifications of NEMA 17
The specifications for a 6-wire 2-phase (4V,1.2A) NEMA 17 stepper motor are listed in the table below:
| Parameter | Value |
| Voltage | 4V |
| Rated Current/phase | 0.95A |
| Step Angle | 1.8° |
| No. of Phases | 4 |
| Phase Resistance | 3.3ohm |
| Inductance | 4mH |
| Length | 33mm |
| Rotor Inertia | 35g-cm2 |
| Shaft Diameter | Φ5mm |
| Shaft Length | 22mm |
| Frame size | 42 x 42mm |
| Unipolar Holding Torque | 2.59kg-cm(36oz-in) |
| Resistance Accuracy | 10% |
| Inductance Accuracy | 20% |
| Step angle Accuracy | ±5% (full step, no load) |
| Temperature Rise | 80°C Max. (rated current,2 phase on) |
| Ambient Temperature | -10°C ~ +50°C |
| Insulation Resistance | 100MΩ Min. 500 VDC |
| Dielectric Strength | 500 VAC•5mA for one minute |
| Shaft Radial Play | 0.06 Max. (450 g-load) |
| Shaft Axial Play | 0.08 Max. (450 g-load) |
NEMA 17 stepper motor dimensions
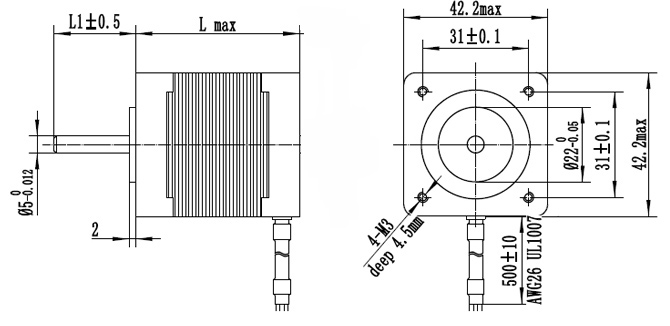
NEMA 17 motor has a faceplate dimensions of 1.7 by 1.7 inches (43 mm × 43 mm). Depending on the manufacturer, the other dimensions of the motor may change, but the faceplate dimensions remain the same.
As for the above-discussed 6-wire 2-phase (4V,1.2A) NEMA 17 stepper motor the motor length is 33mm, the shaft diameter is Φ5mm, and the shaft length is 22mm. If we take the same motor from a different manufacturer, these values may be different.
NEMA 17 stepper motor pinout
Based on the model, a NEMA 17 stepper motor may have 4, 5, or 6 wires. The models with 5, and 6 wires are unipolar stepper motors, while the model which has 4 wires is a bipolar stepper motor.
Unipolar motors
A unipolar stepper motor has two sets of winding placed perpendicular to each other. This arrangement of windings creates a rotating magnetic field for the rotor.
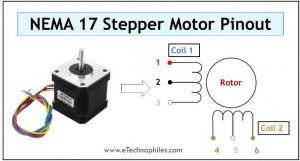
6 Wire Stepper Motor
If center tap are taken from each coil winding, the motor becomes a 6 wire stepper motor and the arrangement thus obtained is shown in the figure below. Using this method, we have created four phases instead of two. Now each section of this winding can be energized, based on the step angle required for the rotor.
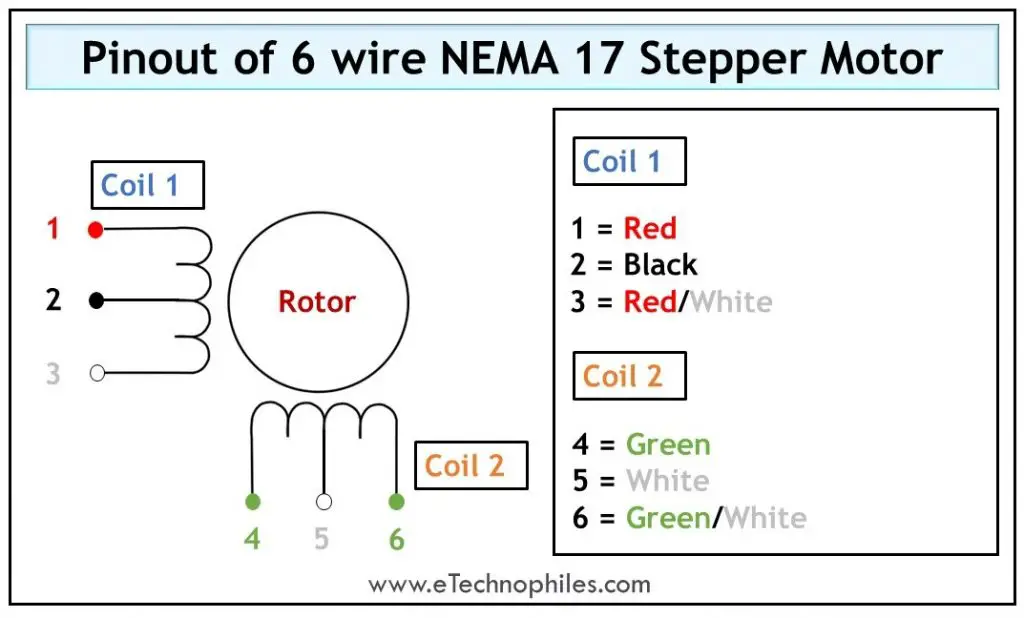
The table below gives the pinout of a 6-wire stepper motor.
| Wire Number | Wire type | Wire color |
| 1 | The first end of Coil 1 | Red |
| 2 | Centre-tap | Black |
| 3 | The second end of Coil 1 | Red/White |
| 4 | The first end of Coil 2 | Green |
| 5 | Centre-tap | White |
| 6 | The second end of Coil 2 | Green/White |
5 Wire Stepper Motor
In the above construction, each center tap serves as a common wire, for two phases. But, if we connect both of the center taps together to create a common wire for all four phases, the controlling becomes easier. Thus the motor becomes a 5-wire stepper motor whose winding arrangement is shown in the figure below.
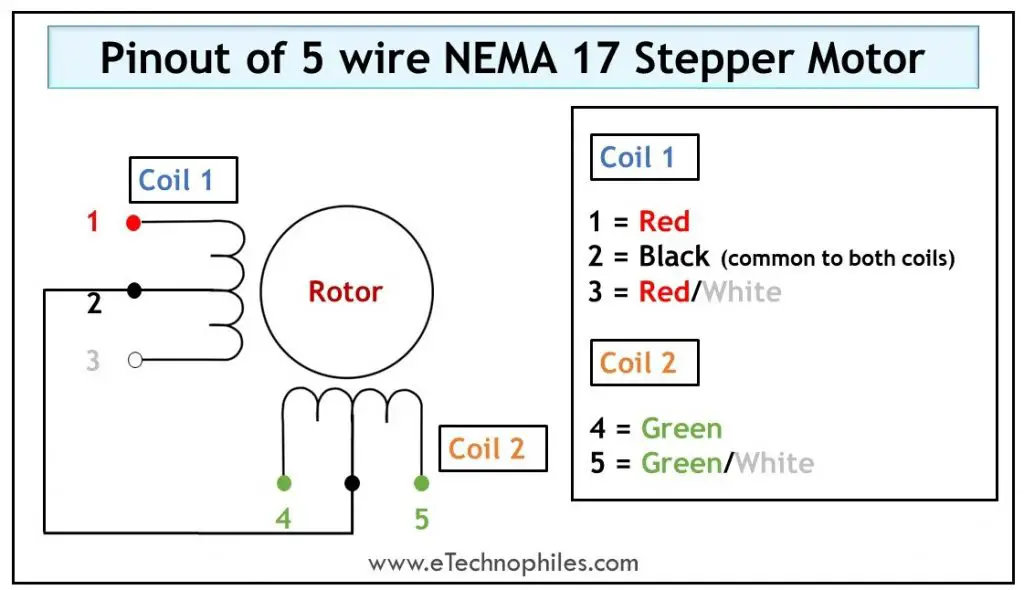
The table below gives the pinout of a 5-wire stepper motor.
| Wire Number | Wire type | Wire color |
| 1 | The first end of Coil 1 | Red |
| 2 | Centre-tap (common to both coils) | Black |
| 3 | The second end of Coil 1 | Red/White |
| 4 | The first end of Coil 2 | Green |
| 5 | The second end of Coil 2 | Green/White |
Bipolar motors
The bipolar stepper motors have only two sets of windings with no center taps, thus it has only 4 wires. Controlling a bipolar motor becomes difficult because it requires an H-bridge arrangement to reverse the direction of current in a winding. (Read more)
The winding arrangement of a 4-wire stepper motor is shown in the figure below.
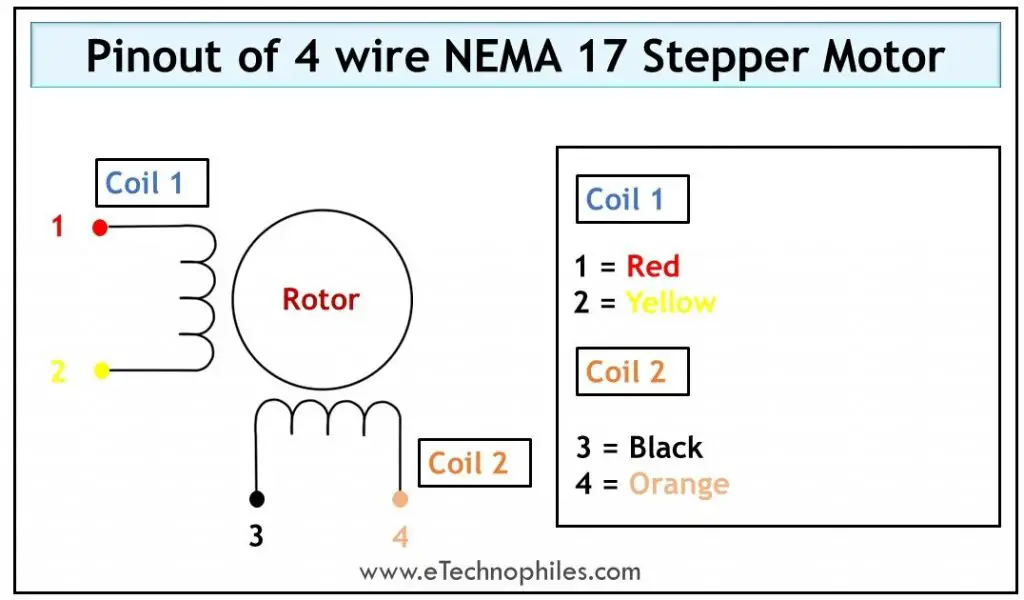
The table below gives the pinout of a 4-wire stepper motor.
| Wire Number | Wire type | Wire color |
| 1 | The first end of Coil 1 | Red |
| 2 | The second end of Coil 1 | Yellow |
| 3 | The first end of Coil 2 | Black |
| 4 | The second end of Coil 2 | Orange |
Note: The color of the wire representing each coil/center tap may not be true for all models. Depending on the manufacturer and the type of model, the color of the wires may be different.
Applications of NEMA 17 stepper motor
As discussed above, NEMA 17 stepper motors have a high holding torque. Even though some of the motors have an open-loop system, their precision is high and is suitable for high torque and low-to-medium acceleration applications. Some of the common applications of these motors are:
- Fax machines
- Small robotics
- Gaming machines
- Medical imaging machinery
- Copiers
- 3D printing equipment
- Textile machines
- CNC milling machines
- Printing presses
NEMA 17 stepper motor datasheet
As discussed above, a NEMA 17 stepper motor is manufactured by different manufacturers. If you are looking for general and electrical specifications for different models of NEMA 17, click here.
To download the datasheet of the NEMA 17 Stepper Motor manufactured by Schneider Electric, click here.
FAQs
What is the RPM of the NEMA 17 stepper motor?
Stepper motors are designed to run best approximately at 1200 RPM or lower. Although it is possible to increase the speed of a small stepper motor with a higher-powered controller, it will reduce the lifespan of the motor.
Note: In a stepper motor, the highest torque is generated at zero speed. However, torque falls off as the speed increases.
The maximum speed at which an open-loop NEMA 17 stepper motor can run is 2000 RPM. But, the recommended speed range is 200-600 RPM. While for a closed-loop NEMA 17 stepper motor, the maximum speed is 3000 RPM. For this, the recommended speed range is 200-700 RPM.
How strong is a Nema Stepper Motor?
A motor is considered robust if it provides high-holding torque. For different versions of the NEMA 17 stepper motor, the holding torque varies from 2 kg-cm to 5 kg-cm. While the current ranges from 0.7 Amps to 1.7 Amps. Due to higher torque, these motors are used in 3D printers, CNC machines, robotics, and other industrial applications.
Are all NEMA 17 Stepper motors the same?
The NEMA numbers signify the standard dimensions of the faceplate mounting the motor. It does not specify any other characteristics of the motor. This means that if there are two different NEMA 17 motors, they may have completely different technical specifications and may not be used as a substitute for one another.
The NEMA standardization provides interchangeability, i.e., the ability to switch from one manufacturer to another without the hassle to change different parts of the motor such as couplings, mounting brackets, etc. But, if we take a NEMA 17 stepper motor designed by two different manufacturers, there is a chance that these two motors can have different electrical or mechanical specifications. Such as shaft length and shaft diameter, the number of lead wires, and many more.
So consider all the specifications of a NEMA Stepper motor, from two different manufacturers before installing the motor in any application.
What does NEMA 17 stand for?
The number after the NEMA motors gives us the nameplate dimensions of the motor. In general, for a NEMA XX motor, dividing XX by 10 will give you the diameter of the faceplate in inches. Hence, the NEMA 17 stepper motor has a diameter of 1.7 inches. The dimensions of the NEMA 17 stepper motor are 1.7 by 1.7 inches (43 mm × 43 mm).
Do 3D printers use Stepper or Servo Motors?
Generally, 3D printers use stepper motors due to their simple, and precise control. This is because the stepper motors have an open loop system. A limit switch can be used to create a home position of the stepper motor and thus, by counting the step pulses, the motor movement can be controlled.
On the other hand, the servo motors work on a closed-loop system. They require constant feedback to control the position of the print head. Thus, it requires complicated hardware and the controlling becomes difficult.
But yes, we can control the 3D printers with servo motors also.
Is NEMA 17 Bipolar or Unipolar?
NEMA 17 stepper motor can either be a unipolar or bipolar stepper motor. By checking the specifications of the motor, you can find that out. One easy way to confirm this is by counting the number of wires available to control the motor. If there are four wires, the motor is a bipolar stepper motor. And if the number of wires is five or six, then it is a unipolar stepper motor.