Last updated on April 2nd, 2024 at 11:49 am
TVS diode or Transient voltage suppression diode is also known as clamp diode, transil, or thyrector. It is an essential component in power electronics design circuits used for handling transient spikes.
In this article, we will cover its basics, working, symbol, VI characteristics, and how it is different from a Zener diode.
Table of Contents
What is a TVS diode?
They are designed to protect electronic circuits from transients and overvoltage threats such as EFT (electrically fast transients), ESD (electro-static discharge), inductive load switching, and even lightning strikes. They are silicon avalanche devices with fast response time, low capacitance, low leakage current, and low clamping voltage.
Note: TVS diode is often considered a type of Zener diode that utilizes TVS characteristics in the breakdown region. Though they both work in the breakdown region, their construction and application are different.
Transients, which are sudden spikes in voltage or current, can harm a circuit in different ways. These range from millivolts to thousands of volts and can occur from a few nanoseconds to hundreds of milliseconds. Transients occur due to internal and external connections in the circuit. Transients may occur once or repeat depending on the conditions.
Symbol
They are of two types- Unidirectional and Bidirectional TVS diode. Their symbol is given below:
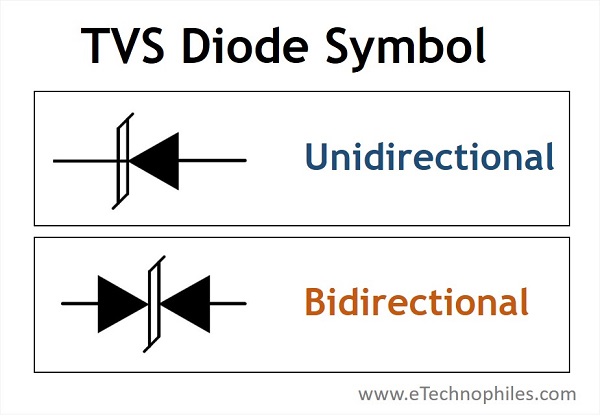

Unidirectional TVS diode
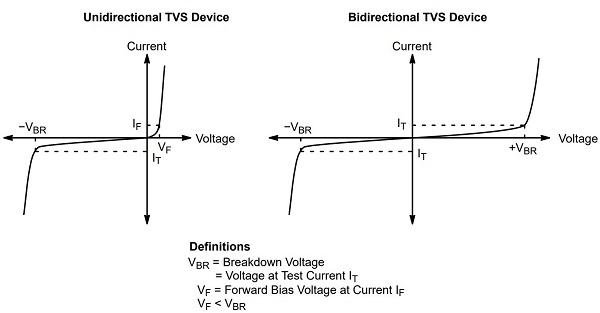
Unidirectional means it works as a normal rectifier diode when forward-biased. The only difference is that it is used specifically for overvoltage spike protection in one direction(reverse-biased) and can handle very large peak currents.
That is why, in reverse-biased mode, it only acts as a clamping device for positive voltages.
Bidirectional TVS diode
A bidirectional TVS diode consists of two unidirectional diodes connected in series and can operate in both directions as needed. It has a symmetrical breakdown voltage in both forward and reversed biased directions and so it works as a clamping device for both positive and negative voltages.
How does a TVS diode work?
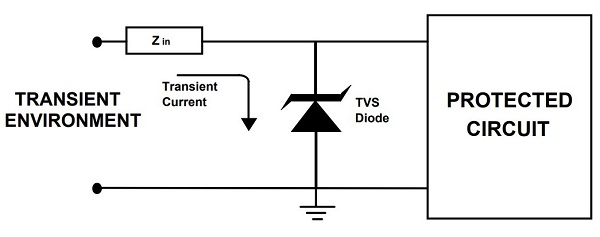
In the image above, the diode is connected in parallel with the circuit under protection. It works on the principle of avalanche breakdown in reverse bias mode, suppressing all voltage spikes above its breakdown voltage.
There are two modes of operation of this diode in a circuit.
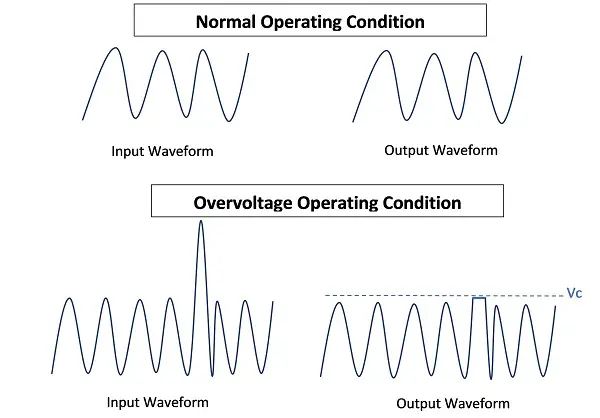
Normal operating mode: When there is no voltage spike, it acts like a normal diode in reverse bias mode, as an open circuit with negligible leakage current.
Under normal conditions, a TVS diode acts as a capacitor with very small capacitance.
Overvoltage operating mode: When a transient spike occurs, the diode immediately goes into the breakdown region. In this region, it has a very low impedance, providing a short path for the high transient current. As a result, most of the transient current passes through the TVS diode, thus protecting the load.
Applications
They are designed to protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes and transients. They are used in various applications such as:
- Surge protection for power lines or communication lines, such as telephones, modems, and LANs.
- In automotive industries where they are used to protect the car’s delicate sensitive electronic components from short circuits and overvoltage.
- Electronic devices, such as mobile phones, TVs, etc., to protect their delicate components from voltage spikes.
- Surrounding a transistor in an amplifier circuit to protect it from any possible damage due to overvoltage or transient voltages.
Zener vs TVS diode
People often think both these diodes are the same, but they serve different purposes and are made differently.
- Zener diodes help to regulate voltage and operate in the breakdown region, while TVS diodes are designed specifically to suppress transient overvoltage spikes. Hence its electrical properties are more suited for this kind of application.
A TVS diode typically has a high impedance, meaning that only very little current(called leakage current) flows through it when reverse-biased. So it only conducts when there is a voltage transient that exceeds its avalanche breakdown voltage.
- The second most important difference between TVS and Zener diode is its fast reaction time. We know that transients occur anywhere from picoseconds to nanoseconds, so the response time of this diode must be very short.
- It offer a wide range of operating voltages to accommodate the highest possible transient spikes in any electrical and electronic circuit.
So overall, TVS is more efficient than Zener diode in terms of properties like low clamping voltage, high operating voltage, low capacitance, less leakage current, and very fast response time.
FAQs
What is the difference between TVS and Zener diodes?
TVS diodes protect against voltage spikes by diverting excess voltage, with high ratings and fast response times, used in surge-prone applications. Zener diodes regulate voltage across terminals, maintaining a constant voltage over a wide current range, commonly employed in voltage regulation circuits.
How to use a TVS diode for ESD protection?
To ensure protection, they are predominantly placed on signal lines, typically between a connector and an IC, with one side connected to the signal line and the other side to the ground. During normal operation, the diode appears as an open circuit, only conducting during voltage spikes to divert excess energy safely to the ground.
How do TVS diodes fail?
They can fail due to overvoltage, overcurrent, degradation over time, manufacturing defects, incorrect application, and thermal issues. To prevent failure, choose diodes with suitable ratings, ensure proper installation, and monitor for signs of stress or degradation.