Last updated on August 21st, 2024 at 11:02 am
2N2222 is an NPN – BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) which means that in between the two N-doped layers, there is a single P-doped layer embedded with it.
2N2222 is a current-controlled transistor. Thus, a low current at the base terminal can be used to drive a high current between two other terminals.
It is used for switching applications or low power amplifying. It can also be used for pulse width modulation as its response time is fast.
Note: 2N2222A Transistor is the TO-92 plasitic enclosure version of 2N2222 with better absolute maximum ratings; Veb, Vcb, and Vce. Some companies call 2N2222 transistor "2N2222A' now and manufactures 2N2222A only.
Table of Contents
Note: PN2222 Transistor is a cheaper version of 2N2222. It also comes in the plastic TO-92 packaging.
Pinout
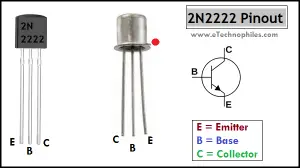
The pinout diagram of 2N2222 shows that there are three pins: emitter, base, and collector respectively from left to right(flat side with the leads pointed downward).
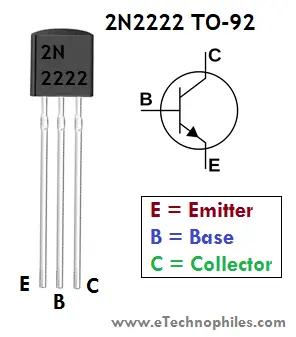
Note: Give above is the pinout of PN2222/2N2222A Transistor, the TO-92 version of 2N2222. PN2222 is not mentioned in the pin diagram in order to keep things simple.
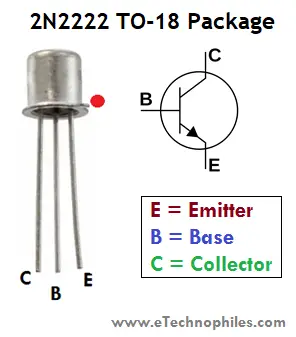
| Pin | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Collector | This pin act as an inlet as the current enters the transistor from here. The collector is denoted by ‘C’. |
| 2 | Base | This pin controls the transistor biasing. The base is denoted by ‘B’. |
| 3 | Emitter | This pin act as an outlet and the current comes out of the transistor from here. The emitter is denoted by ‘ E’. |
2N2222 VS 2N2222A: What’s the difference?
Both are similar types of transistors but the 2N2222A has higher Maximum absolute ratings than 2N2222. The Collector to Base, Collector to Emitter, and Emitter to Base voltage ratings of 2N2222 and 2N2222A are 60V, 30V, 5V and 75V, 40V, 6V respectively.
Also, the 2N2222 comes in metal packaging whereas the 2N2222A is available in TO-92 plastic enclosure only.
2N2222A is a better option considering its higher ratings, low cost, and TO-92 packaging.
Specifications
The technical specifications of 2N2222 in TO-18 metal packaging and 2N2222A transistor in TO-92 packaging are given below:
| Spec | 2N2222A | 2N2222 |
| Power Dissipation(TC = 25°C) | 1.5 | 1.2W |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 30-300 | 30-300 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55 to 150°C | -65 to 200°C |
| Continuous Collector Current (IC) | 0.6 A | 0.8 mA |
| Collector-Base Voltage(VCB) | 75 | 60V |
| Emitter-Base Voltage(VEB) | 6 | 5V |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage(VCE) | 40 | 30V |
| Input Capacitance(CI) | 25pF | 30pF |
| Output Capacitance(CO) | 8pF | 8pF |
| Transistor type | NPN | NPN |
| Package | TO-92 | TO-18 |
| Mounting Type | Through-hole | Through-hole |
| Transition frequency(Ft) | 250MHz |
The exact specifications depend on the manufacturer, case type, and variation. Therefore, it is important to refer to the datasheet for the exact part number and manufacturer.
Which transistors are equivalent to 2N2222?
Given below is the list of transistors that are equivalent to 2N2222 and can be used as a replacement.
Can a BC547 be replaced with 2N2222?
Yes, we can replace BC547 with 2N2222. BC547 transistor is considered the best equivalent of 2N2222 & can work well in your projects. Although using an equivalent transistor requires a detailed comparison, the BC547 is still a good alternative to 2N2222.
Are there any differences between 2N2222 and BC547 Transistor?
Between BC547 & 2N2222, there are minor changes in output and input capacitance. The input and output capacitance of 2N222 is slightly higher than BC547. This affects the circuit while operating at a higher frequency.
Other differences between both transistors are given below:
| Spec | 2N2222 | BC547 |
|---|---|---|
| Collector to Base voltage | 60V | 50V |
| Collector to Emitter voltage | 30V | 45V |
| Emitter to Base voltage | 5V | 6V |
| Maximum collector current | 800mA | 100mA |
| DC Gain | 75-300HFe | 110-800HFe |
| Thermal resistance | 146k/w | 83.3°C/w |
| Transition frequency | 250MHz | 300MHz |
| Noise figure | 4db | 10db |
Uses and applications
2N2222 is used in a variety of electronic projects due to its excellent features like a larger collector current 600mA. This feature makes it ideal for electronics projects like controlling high-power LEDs, relays, high-power transistors, and ICs.
The applications of this transistor are:
- Motor driver circuits
- Switching circuits
- Amplifier circuits
- Sensors circuits
- Audio preamplifier
- Low power application
- Inverter circuits
- RF circuits
- Darlington Pair
- Embedded and automation projects
Datasheet of 2N2222 transistor
Given below is the datasheet in the TO-18 Metal can package:
Download 2N2222 TO-18 package datasheet
Given below is the datasheet in the TO-92 package:
Download P2N2222A TO-92 package datasheet
This transistor has several variants collectively called as “2N2222 type” and they are identical to the original 2N2222 transistor in terms of operation and functionality.
Among these transistors, P2N222A is the main transistor, which is available in the TO-92 package made of either plastic or epoxy. Due to its number of advantages and low cost, the TO-92 package of P2N222A has become the most used and cost-effective transistor in electronics.
Where to buy 2N2222(TO-18)?
You can easily find these transistors in your local electronics store. For online purchases, we recommend this best deal on Amazon:
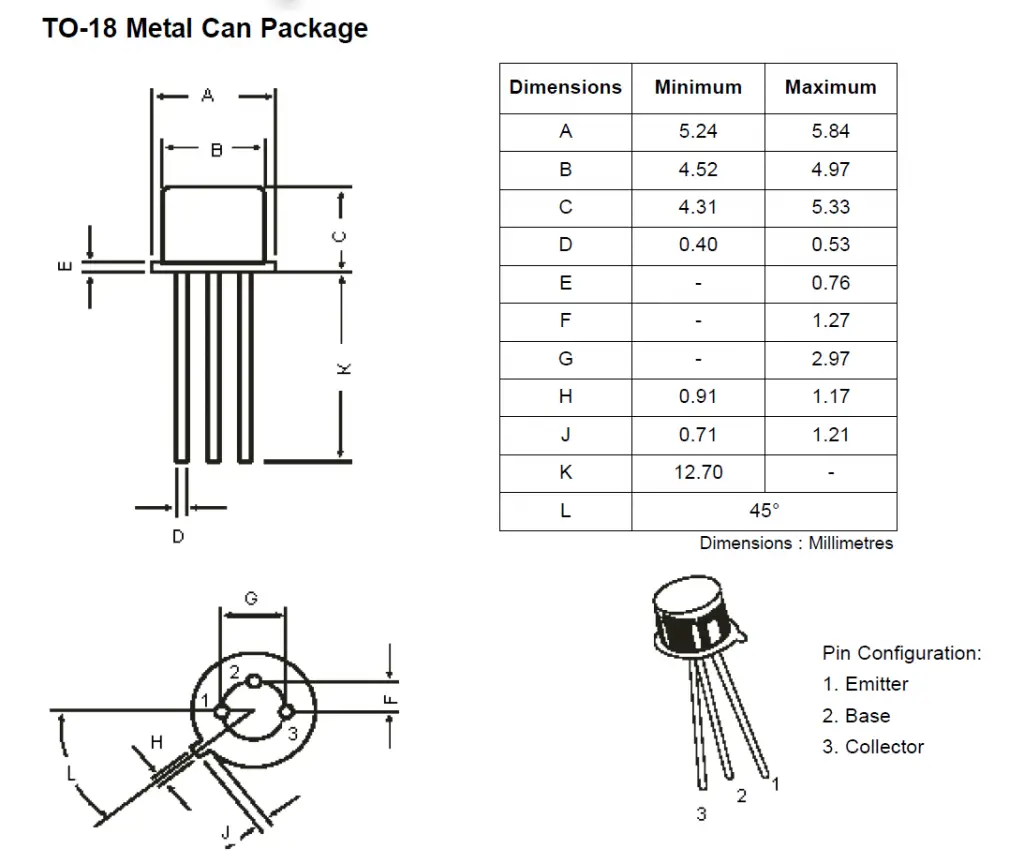
Dimensions
Given below are the dimensions of its TO-18 package. All the dimensions are in mm.

Thank you! Found this quite useful in comparing several of the above transistors.
You have appear to have mixed up Emitter and Collector definitions.
1 Emitter This pin act as an inlet as the current enters the transistor from here. The collector is denoted by ‘C’. <—-
2 Base This pin controls the transistor biasing. The base is denoted by ‘B’.
3 Collector This pin act as an outlet and the current comes out of the transistor from here. The emitter is denoted by ‘ E’. <—-
Hi Terry,
Thank you for bringing this to our attention. It’s corrected now.
You must have failed to fix that mixup when you were stating the voltage limits IN THE TEXT (you got it right in the table). In the text you swap the emitter-to-base and collector-to-emitter values, compared to the table. And the table ones look right to me.
Hi Kip,
Thank you for pointing out the error. We really appreciate it.
We have corrected the specs now 🙂