Last updated on April 5th, 2024 at 11:31 am
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a display standard that carries video signals as analog components. IBM developed it in 1987 to use in their PCs (PS/2). The VGA connectors are usually used to connect a computer to a Monitor or projector, provided, the computer has a VGA port.
Since it supports only analog data, the VGA connectors are now replaced by digital interfacing standards like HDMI and DisplayPorts. In this article, we will discuss VGA pinout and its specifications.
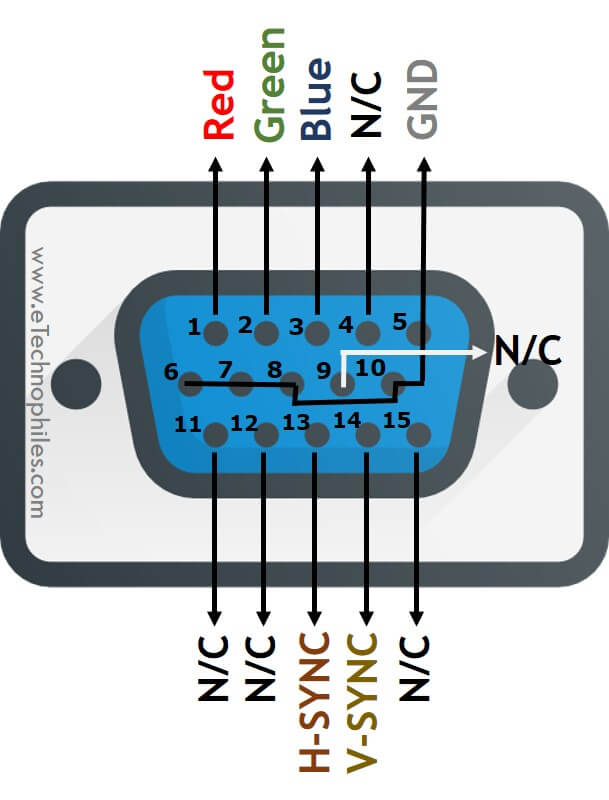
VGA connector pinout
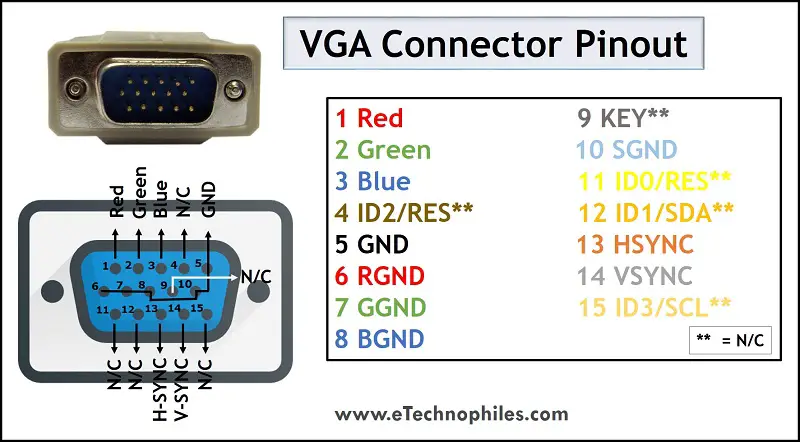
VGA standard has a 15-pin connector. The pins are arranged in 3 rows, each raw consisting of 5 pins. Apart from the regular insertion, the connector has a screw-type locking mechanism. The pin description of the VGA connector is listed in the table below.
| Pin number | Pin name | Pin description |
| 1 | Red | Red video |
| 2 | Green | Green video |
| 3 | Blue | Blue video |
| 4 | ID2/RES(N/C) | Monitor ID Bit 2 / Reserved |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | RGND | Red Ground |
| 7 | GGND | Green Ground |
| 8 | BGND | Blue Ground |
| 9 | KEY(N/C) | +5V DC output from graphic card |
| 10 | SGND | Sync Ground |
| 11 | ID0/RES(N/C) | Monitor ID Bit 0 / Reserved |
| 12 | ID1/SDA(N/C) | Monitor ID Bit 1 / I2C bi-directional data line |
| 13 | HSYNC | Horizontal Sync |
| 14 | VSYNC | Vertical Sync |
| 15 | ID3/SCL(N/C) | Monitor ID Bit 3 / I2C data clock |
Separate pins are allocated for Red, Green, and Blue components. These are the primary colors. The other two components of video data are horizontal sync and vertical sync. Hence, the analog video signal is transmitted as RGBHV components VESA DDC (Video Electronics Standards Association Display Data Channel ) data. The VESA DDC pins are used in modern VGA connectors to identify the connected display device.
The RGB component pins are placed in the top row, and HSync and VSync are in the bottom row. The entire middle row is allocated for the respective ground connections except for pin 9.
Connector specifications

Among the different nomenclatures of VGA connectors such as D-sub-15, mini sub D15, mini D15, DB-15, HDB-15, HD-15, and HD15, the most common VGA connector (explained here) falls under DB-15. The smaller-sized connectors are used with small devices, but the DB-15 connector is the most widely used.
The regular resolution of color display screens supported by VGA is 640 x 480px @60 Hz refresh rate where 16 colors are backed at a time. The maximum resolution supported is 2048 x 1536px @85 Hz. The safe range of cable length available in VGA (without signal loss) is 0.75 feet to 30 feet.
Advantages
Some of the advantages of VGA cables are listed below:
- The VGA connectors are cheap and easily available.
- The connectors are manufactured with high-quality materials.
- The cables come with double and sometimes, triple shielding.
- A separate ground shield is given for red, green, and blue data pins.
- Two alternating clock pins are provided for communicating with the connected devices.
Read also: 5 HDMI Types & 7 Standards Explained(Speed Compared)
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of VGA cables are listed below:
- The biggest disadvantage of VGA is that it does not support digital data, while most modern devices have digital signaling.
- It only transfers video signals. Separate interfacing should be given for audio signals.
- There are huge chances of signal loss and reduced resolution since the transmitted signal is analog.
- The connector is not hot-pluggable.
- The aspect ratio maintained by the VGA standard is 4:3, but that of modern displays is 16:9.
