Last updated on March 21st, 2024 at 12:37 pm
In early 2011, Apple became the first manufacturer to use Intel’s Thunderbolt technology; which is an external data port that can be plugged into any computer for high-speed transfers.
It was initially called Light Peak because Intel intended it to rely on fiber optics; hence the reference to light in the name. As Intel developed its product, it got a new name: Thunderbolt.
The Thunderbolt 1 and 2 have 20 pins whereas Thunderbolt 3 and 4 have 24 pins.
Table of Contents
Thunderbolt 1 and 2 pinout
Thunderbolt 1 was launched in the year 2011, while Thunderbolt 2 was launched in the year 2013. Both Thunderbolt 1 and Thunderbolt 2 have the same connector, which is similar to that of DisplayPort. While the speed of Thunderbolt 1 is limited to 10 Gbps per channel, Thunderbolt 2 gives 20 Gbps speed per channel. (Read more)
Both have a 20-pin connector as shown in the figure below.
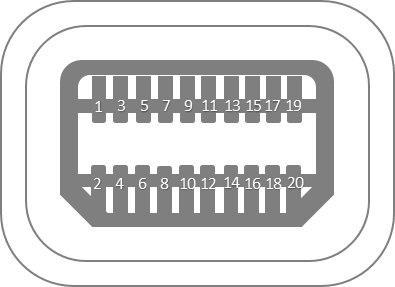
The table below gives the pinout of the Thunderbolt 1 and 2 connectors.
| Pin Number | Pin | Description |
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | HPD | Hot Plug Detect |
| 3 | HS0TX+ | HighSpeed transmit 0 (+) |
| 4 | HS0RX+ | HighSpeed receive 0 (+) |
| 5 | HS0TX- | HighSpeed transmit 0 (-) |
| 6 | HS0RX- | HighSpeed receive 0 (-) |
| 7,8 | GND | Ground |
| 9 | LSR2P TX | LowSpeed Transmit |
| 10 | GND | Ground (reserved) |
| 11 | LSR2P RX | LowSpeed receive |
| 12,13,14 | GND | Ground |
| 15 | HS1TX+ | HighSpeed transmit 1 (+) |
| 16 | HS1RX+ | HighSpeed receive 1 (+) |
| 17 | HS1TX- | HighSpeed transmit 1 (-) |
| 18 | HS1RX- | HighSpeed receive 1 (-) |
| 19 | GND | Ground |
| 20 | DPPWR | Power |
Thunderbolt 3 and 4 pinout
The upgraded version of Thunderbolt, which is Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 uses the USB Type – C connector which has 24 pins. Thunderbolt 3 was launched in the year 2015, while Thunderbolt 4 was launched in the year 2020. Both have a speed of 40 Gbps.
The pinout of Thunderbolt 3 and 4 is given in the figure below.
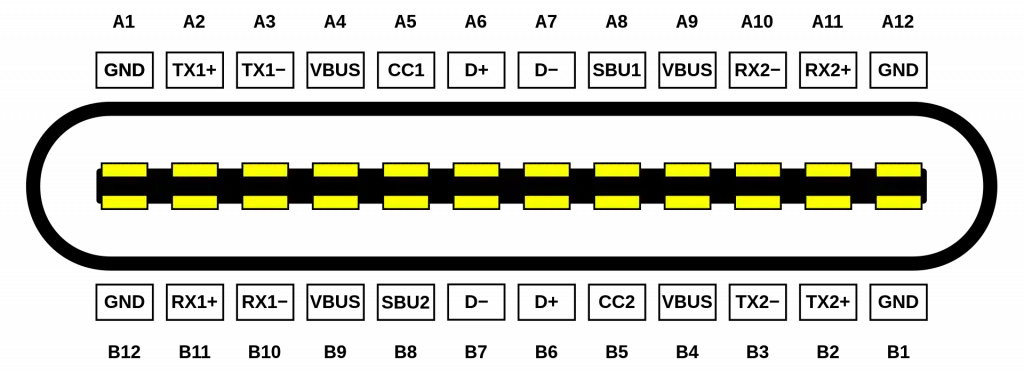
| Pin | Description | Pin | Description |
| A1 | Ground | B12 | Ground |
| A2 | SuperSpeed differential pair 1, TX, positive | B11 | SuperSpeed differential pair 2, RX, positive |
| A3 | SuperSpeed differential pair 1, TX, negative | B10 | SuperSpeed differential pair 2, RX, negative |
| A4 | Bus power | B9 | Bus power |
| A5 | Configuration channel | B8 | Side Band Use (SBU) |
| A6 | Differential pair 1, positive | B7 | Differential pair 2, negative |
| A7 | Differential pair 1, negative | B6 | Differential pair 2, positive |
| A8 | Side Band Use (SBU) | B5 | Configuration channel |
| A9 | Bus power | B4 | Bus power |
| A10 | SuperSpeed differential pair 4, RX, negative | B3 | SuperSpeed differential pair 3, TX, negative |
| A11 | SuperSpeed differential pair 4, RX, positive | B2 | SuperSpeed differential pair 3, TX, positive |
| A12 | Ground | B1 | Ground |
For a detailed comparison between all 4 types read this article: Difference Between 4 Types of Thunderbolt (1,2,3,4)
Thunderbolt features
Thunderbolt is one of the most advanced versions among the available ports. Some of the features that make it stand out are discussed below:
- It is designed to support several other standards like USB Type C, DisplayPort, PCIe, etc. Hence the input/output devices in any of these standards are good to interface via Thunderbolt connections.
- It supports two 4K monitors simultaneously with a speed of 10Gbps, which is simply amazing and endorsing, especially for gamers.
- It is the fastest peripheral interface that achieves the data transfer speed in the range of 10Gbps to 40Gbps which is several times larger than the other available peripherals.
- These cables are capable of delivering power up to 100W so that they can charge devices that even require a significant power range, like laptops.